Maui residents who made desperate escapes from oncoming flames, some on foot, asked why Hawaii’s famous emergency warning system didn’t alert them as fires raced toward their homes.
Hawaii emergency management records show no indication that warning sirens were triggered before a devastating wildfire killed at least 55 people and wiped out a historic town, officials confirmed Thursday.
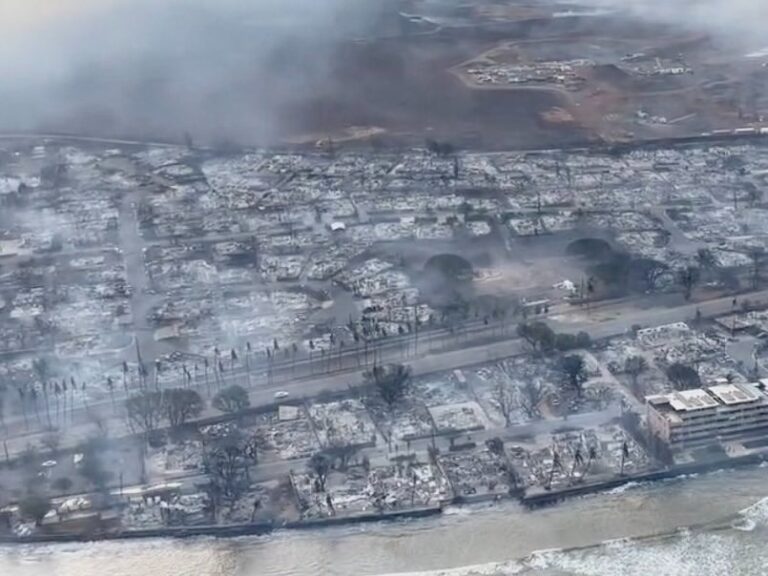
Hawaii boasts what the state describes as the largest integrated outdoor all-hazard public safety warning system in the world, with about 400 sirens positioned across the island chain. But many of Lahaina’s survivors said in interviews at evacuation centers that they didn’t hear any sirens and only realized they were in danger when they saw flames or heard explosions nearby.
Thomas Leonard, a 70-year-old retired mailman from Lahaina, didn’t know about the fire until he smelled smoke. Power and cell phone service had both gone out earlier that day, leaving the town with no real-time information about the danger. He tried to leave in his Jeep, but had to abandon the vehicle and run to the shore when cars nearby began exploding. He hid behind a seawall for hours, the wind blowing hot ash and cinders over him.
Firefighters eventually arrived and escorted Leonard and other survivors through the flames to safety.
Hawaii Emergency Management Agency spokesperson Adam Weintraub told The Associated Press on Thursday that the department’s records don’t show that Maui’s warning sirens were triggered on Tuesday. Instead, the county used emergency alerts sent to mobile phones, televisions and radio stations, Weintraub said.
It’s not clear if those alerts were sent before widespread power and cellular outages cut off most communication to Lahaina.
Fueled by a dry summer and strong winds from a passing hurricane, the fire started Tuesday and took Maui by surprise, racing through parched brush covering the island and then flattening homes and anything else that lay in its path.
The wildfire is already the state’s deadliest natural disaster since a 1960 tsunami, which killed 61 people on the Big Island. During a Thursday press conference, Gov. Josh Green said the death toll will likely rise further as search and rescue operations continue.
“Lahaina, with a few rare exceptions, has been burned down,” Green said after walking the ruins of the town Thursday morning with Maui Mayor Richard Bissen. “Without a doubt, it feels like a bomb was dropped on Lahaina.”
The fire is also the deadliest U.S. wildfire since the 2018 Camp Fire in California, which killed at least 85 people and laid waste to the town of Paradise.
Lahaina’s wildfire risk was well known. Maui County’s hazard mitigation plan, last updated in 2020, identified Lahaina and other West Maui communities as having frequent wildfire ignitions and a large number of buildings at risk of wildfire damage.
West Maui was also identified as having the island’s highest population of people living in multi-unit housing, the second-highest rate of households without a vehicle, and the highest rate of non-English speakers.
“This may limit the population’s ability to receive, understand and take expedient action during hazard events,” the plan noted.
Maui’s firefighting efforts may also have been hampered by a small staff, said Bobby Lee, the president of the Hawaii Firefighters Association. There are a maximum of 65 firefighters working at any given time in Maui County, and they are responsible for fighting fires on three islands – Maui, Molokai and Lanai – he said.
Abc7ny